The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive expands the scope of the Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD) and introduces more detailed reporting requirements for companies. The European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) are a set of 12 standards that outline reporting requirements for companies in-scope for the CSRD. In general, the ESRS require companies to disclose sustainability data, targets or goals around sustainability performance, and methodologies and assumptions for calculating disclosed metrics based on the results of a double materiality assessment. To comply, companies will need to navigate a complex web of EU regulations and voluntary frameworks that extend beyond the CSRD.
ESRS 1 outlines general requirements and parameters of reporting to CSRD. ESRS E1, in particular, covers requirements as they relate to climate change. To help companies complying with the ESRS E1, below are key highlights of the requirements under the standard.
ESRS E1 By The Numbers
The European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) E1 outlines requirements for climate-related reporting under the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD). Novata’s analysis broke down the requirements to highlight key learnings.

- 9: Number of disclosure requirements under the ESRS E1 Climate Change Standard
- 27%: Disclosure requirements that have companies report Goals and Targets related to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. E.g., GHG Emission Reduction Targets (companies are expected to align GHG reduction targets with the EU Taxonomy Regulation or explain the absence of such targets) and the TCFD Metrics and Targets Pillar.
- 36%: Disclosure requirements that have companies report a process or policy in place related to GHG emissions. E.g., TCFD Risk Management Pillar, Complete a GHG Inventory, TCFD Scenario Analysis, Disclosure of use of Carbon Credits and Internal Carbon Pricing
- 64%: Disclosure requirements that have companies sifting through complex EU regulations beyond ESRS E1. E.g., SFDR PAIs are referenced in 50% of requirements.
- 100%: Disclosure requirements that have companies sifting through guidance from voluntary ESG frameworks and standards.
Building ESRS Readiness
Compliance with the ESRS E1 standard requires companies to be capable in carbon data collection and have a good understanding of various EU regulations, voluntary standards, and frameworks. For many, keeping abreast of the various requirements will be a significant challenge, alongside confidently measuring their carbon footprint and gathering and disclosing this data to regulators via the European Single Access point.
For companies looking to build readiness around ESRS topics and be ready to comply, Novata can help:
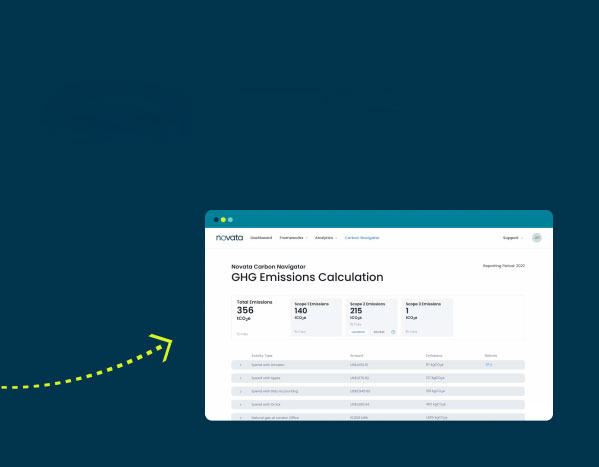
- Carbon Navigator’s methodology is aligned with the CSRD regulation and makes it easy to get started with measuring carbon emissions.
- Carbon-related support from Novata Services improves processes and data quality for greenhouse gas emissions reporting, setting companies up for third-party assurance to CSRD specifications.
- CSRD regulatory readiness with Novata Services identifies and streamlines the process for companies to select relevant ESRS metrics after a double materiality assessment, and ensures client readiness for data collection.
Learn more about how Novata can support your carbon journey.